The training course “Environmental remediation technologies” is aimed at identifying, analysing, designing and evaluating technological and process interventions for the recovery and management of environmental quality.
The design and implementation of processes and infrastructure necessary for the rehabilitation of contaminated environments and the reduction of the impact of civil and industrial activities are disciplinary aspects that, present since the beginning of the professional figure, have always configured the most strictly technical skills and conventionally associated with engineering. The evolution of the problems, initially confined to hygienic-sanitary requirements within the urban settlements, has progressively involved aspects that extend to wide sectors of various adjoining engineering areas, creating the need to have more specialized and qualified skills in the field of specific intervention.
The nature and content of the technical and implementation skills currently required by environmental engineering extends from the disciplines that affect the complex of process and system aspects to those that involve the configuration of plant and infrastructure construction. The identification, evaluation and comparative analysis of the technologies applicable to the purification and reclamation treatments of air, water and soil are representative activities of the design and system sector, while the implementation and construction of the project involve more operational aspects and those of the management, management and monitoring of the plant engineering work.
Important contributions are also required in the field of planning and definition of strategic interventions, where engineering knowledge is a fundamental element in the formulation and comparative assessment of the alternatives available. In this regard, qualifying aspects in the training of the environmental engineer invest the complex knowledge of the system needed to address the problems of saving and recovery of resources and energy, which is very topical both in the macro sector and in that of individual industries, where the organizational needs of production have also extended to the need to adopt appropriate environmental management systems.
The educational path proposed in the field of remediation technologies provides the basic knowledge required for the identification and engineering evaluation of technical interventions that can be adopted for the remediation and protection of environmental resources. The training is integrated with a set of specialist disciplines that punctually deal with the set of qualifying cognitive tools of the works involved in specific sectors of intervention (air, water, soil, civil and industrial waste, production activities), with an overall curriculum aimed at the professional skills required in the different contexts of interest:
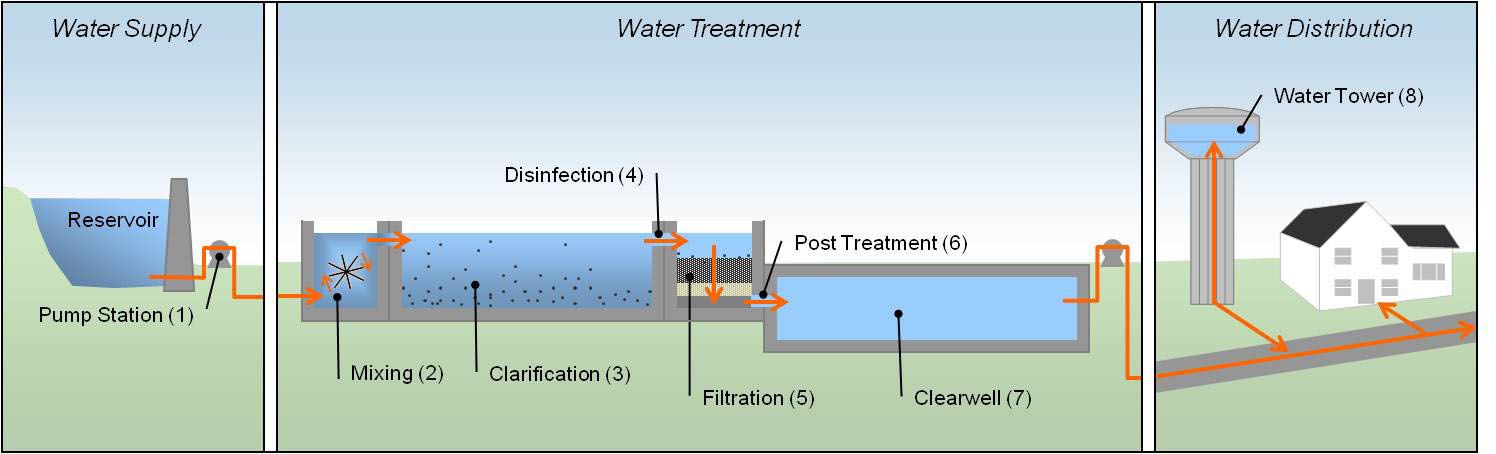
- design, performance analysis and management of technological and plant interventions for the production of drinking and industrial quality water;
- design, performance analysis and management of technological and plant interventions for the treatment of wastewater, gaseous effluents, solid waste, sludge and contaminated sites;
- identification, formulation and design of technological interventions for the recovery and maintenance of quality in the various environmental sectors (water, atmosphere, biosphere, contaminated soils);
- technical evaluations of management strategies and recovery of materials, resources and energy from civil and industrial residues (wastewater, biomass, solid waste and sludge, by-products of processing);
- assessment of the impact on the environment of major works, regulatory plans and new regulations.
The training curriculum of the proposed course configures potential placements in different professional sectors:
- public bodies and services for environmental protection, civil protection, territorial protection and assessment of the environmental compatibility of plans and works;
- authorities and agencies for planning and control of the territory and environmental resources;
- engineering companies, professional firms and companies providing territorial and environmental services;
- division of the environment and/or territory into large companies and energy companies;
- companies and companies managing the technological networks of public utility services;
- companies producing water and waste gas treatment plants, energy production and waste disposal plants
construction and maintenance companies for waste treatment and remediation works; - technical analysis of credit and insurance companies;
- universities, public and private research institutes and bodies.